Robots for mixed case palletising
GEEK+ HAS launched a solution for mixed case palletising, co-developed with WSR Solutions, a provider of warehouse management tools.
The solution combines Geek+ autonomous mobile robots and WSR’s palletising algorithm to process multiple outbound orders.
AMRs move goods between the storage area and picking station. At the picking station, WSR’s algorithm supports warehouse operators to stack cases of varying weight, height, width, and so on in an optimal way. It aims to streamline processes inside the warehouse and also make efficient use of truck space.
The solution has four key components:
Storage
The storage area is built on multiple layers using high-density racking and bulk lifts for more storage capacity. After inbound processing, pallets of incoming goods (donor pallets) are stored in high-density racking. Donor pallets are then moved horizontally by four-way shuttles and vertically by lifts. The system flexibly solves bottlenecks caused by rapid changes in required throughput. With no need for wires and long installation periods, the number of shuttles can be flexibly adjusted to handle changes in required throughput, and peak values can be changed using the system’s scheduling tool.
Buffer
Upon receiving the outbound order, items of high outbound volume go to a buffer area between the storage area and the workstation. Upon registering an incoming order, a picking robot picks up the donor pallet from the storage area and moves it to the buffer area for temporary storage. At the buffer area, picking robots streamline the movement of pallets, ensuring the smooth supply and optimal sequencing of source pallets to the workstation.
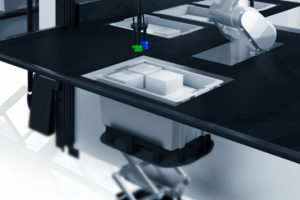
Case Picking
At the workstation, an operator picks cases from a donor pallet and stacks them on an order pallet based on a pre-calculated stacking pattern. The user-friendly interface provides the operator with information on outbound orders such as required type and quantity of goods, and the SAT laser pointer specifies case placement.
If one type of good is included in different orders, picking robots will move the donor pallet of that good to the next workstation, and new donor pallets containing other SKUs will automatically arrive at the previous workstation for continued order picking. The remaining items that do not require further picking will go to the storage area, creating a dynamic transit cycle.
Loading
At the loading area, optimally stacked pallets are loaded onto trucks by autonomous forklifts without the need for re-palletisation. By optimising how pallets are stacked it improves truck space utilisation, lowering the overall transport costs. The algorithm enables efficient organszation and order sequencing of large-scale, mixed case combinations. It can be tailored to fit customers' actual business needs for allocation and priority management, making a powerful tool applicable to a wide range of industry scenarios.
For more information, visit www.geekplus.com